对 TypeScript 装饰器的理解?应用场景?
一、是什么
装饰器是一种特殊类型的声明,它能够被附加到类声明,方法, 访问符,属性或参数上
是一种在不改变原类和使用继承的情况下,动态地扩展对象功能
同样的,本质也不是什么高大上的结构,就是一个普通的函数,@expression 的形式其实是Object.defineProperty的语法糖
expression 求值后必须也是一个函数,它会在运行时被调用,被装饰的声明信息做为参数传入
二、使用方式
由于typescript是一个实验性特性,若要使用,需要在tsconfig.json文件启动,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES5",
"experimentalDecorators": true
}
}
|
typescript装饰器的使用和javascript基本一致
类的装饰器可以装饰:
类装饰
例如声明一个函数 addAge 去给 Class 的属性 age 添加年龄.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| function addAge(constructor: Function) {
constructor.prototype.age = 18;
}
@addAge
class Person{
name: string;
age!: number;
constructor() {
this.name = 'huihui';
}
}
let person = new Person();
console.log(person.age);
|
上述代码,实际等同于以下形式:
1
| Person = addAge(function Person() { ... });
|
上述可以看到,当装饰器作为修饰类的时候,会把构造器传递进去。 constructor.prototype.age 就是在每一个实例化对象上面添加一个 age 属性
方法/属性装饰
同样,装饰器可以用于修饰类的方法,这时候装饰器函数接收的参数变成了:
- target:对象的原型
- propertyKey:方法的名称
- descriptor:方法的属性描述符
可以看到,这三个属性实际就是Object.defineProperty的三个参数,如果是类的属性,则没有传递第三个参数
如下例子:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
function method(target: any, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
console.log(target);
console.log("prop " + propertyKey);
console.log("desc " + JSON.stringify(descriptor) + "\n\n");
descriptor.writable = false;
};
function property(target: any, propertyKey: string) {
console.log("target", target)
console.log("propertyKey", propertyKey)
}
class Person{
@property
name: string;
constructor() {
this.name = 'huihui';
}
@method
say(){
return 'instance method';
}
@method
static run(){
return 'static method';
}
}
const xmz = new Person();
xmz.say = function() {
return 'edit'
}
|
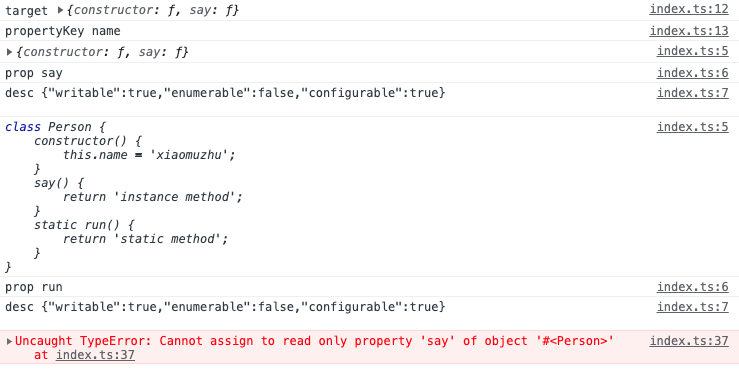
输出如下图所示:
参数装饰
接收3个参数,分别是:
- target :当前对象的原型
- propertyKey :参数的名称
- index:参数数组中的位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| function logParameter(target: Object, propertyName: string, index: number) {
console.log(target);
console.log(propertyName);
console.log(index);
}
class Employee {
greet(@logParameter message: string): string {
return `hello ${message}`;
}
}
const emp = new Employee();
emp.greet('hello');
|
输入如下图:

访问器装饰
使用起来方式与方法装饰一致,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
function modification(target: Object, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
console.log(target);
console.log("prop " + propertyKey);
console.log("desc " + JSON.stringify(descriptor) + "\n\n");
};
class Person{
_name: string;
constructor() {
this._name = 'huihui';
}
@modification
get name() {
return this._name
}
}
|
装饰器工厂
如果想要传递参数,使装饰器变成类似工厂函数,只需要在装饰器函数内部再函数一个函数即可,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| function addAge(age: number) {
return function(constructor: Function) {
constructor.prototype.age = age
}
}
@addAge(10)
class Person{
name: string;
age!: number;
constructor() {
this.name = 'huihui';
}
}
let person = new Person();
|
执行顺序
当多个装饰器应用于一个声明上,将由上至下依次对装饰器表达式求值,求值的结果会被当作函数,由下至上依次调用,例如如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| function f() {
console.log("f(): evaluated");
return function (target, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
console.log("f(): called");
}
}
function g() {
console.log("g(): evaluated");
return function (target, propertyKey: string, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) {
console.log("g(): called");
}
}
class C {
@f()
@g()
method() {}
}
f(): evaluated
g(): evaluated
g(): called
f(): called
|
三、应用场景
可以看到,使用装饰器存在两个显著的优点:
- 代码可读性变强了,装饰器命名相当于一个注释
- 在不改变原有代码情况下,对原来功能进行扩展
后面的使用场景中,借助装饰器的特性,除了提高可读性之后,针对已经存在的类,可以通过装饰器的特性,在不改变原有代码情况下,对原来功能进行扩展
参考文献

